Java String Constant Pool
![]()
🎸 Rocking with Java Strings! 🎸
Welcome to the ultimate Java String jam session! 🎶 Here, we’ll dive into the immutable magic of Strings, groove to the beats of the String Constant Pool, and even uncover the backstage secrets of memory management. Buckle up, because things are about to get string-tastic! 😎
1️⃣ Immutable Strings: The Unbreakable Records 🎤
A String in Java is like your favorite vinyl record—it stays the same no matter how many times you play it! 🎵
Java’s String class is immutable, meaning once you create a string, you CANNOT change it.
Why does Java do this? 🤔
- Security! Sensitive info (like passwords and URLs) stays untouched. 🔒
- Efficiency! The JVM caches strings, reducing memory overhead. 💾
- Stability! No accidental edits that could corrupt your data. 🚀
If Java allowed mutable strings, we’d be rewriting our favorite songs on the fly—and that’s just chaos! 🎸🔥
2️⃣ The String Constant Pool: Java’s VIP Lounge 🎟️
Ever wonder where all your string literals hang out? Welcome to the String Constant Pool (SCP)—a VIP lounge inside the heap memory! 🏰
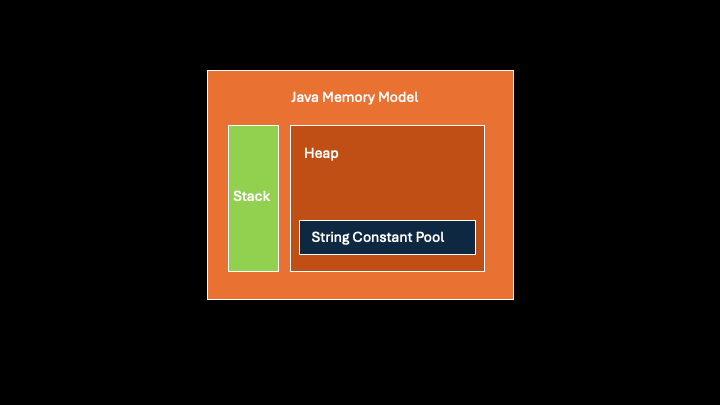
Evolution of the SCP
- Before Java 7 🏛️: SCP lived in the Permanent Generation (PermGen).
- Java 7 & beyond 🚀: SCP moved into the heap.
- Java 8+ 🦾: PermGen is gone, but SCP still thrives inside the heap.
💡 Even though SCP moved, the way Java handles strings hasn’t changed. It’s still optimizing memory usage like a pro! 🎯
3️⃣ String Literals vs. String Objects: The Battle of the Bands 🎶⚔️
String Literals (The Minimalists) 🎷
Literals are stored in the SCP, meaning Java reuses them instead of creating duplicates.
String strLiteral = "Hello World";
String Objects (The Rebels) 🎸
Objects are created in the heap, meaning every new String() call makes a fresh new instance.
String strObj = new String("Hello World");
Who wins? 🤔
If two string literals have the same value, they point to the same reference in SCP. But string objects? They always take up new memory space! 😬
String a = "howtodoinjava";
String b = "howtodoinjava";
System.out.println(a == b); // true 🎉
String c = new String("howtodoinjava");
System.out.println(b == c); // false 🚨
4️⃣ String.intern(): Backstage Pass to SCP 🎫
Want to take a heap string and sneak it into the SCP? Use intern()!
String a = "howtodoinjava";
String b = new String("howtodoinjava");
String c = b.intern();
Now, c will be in SCP along with a, saving memory and making string comparisons super fast! 🚀
5️⃣ Why Java Strings Rock! 🎸🔥
5.1. Enhanced Security 🔐
Immutable strings keep passwords, URLs, and other sensitive info safe from accidental (or malicious) modifications. Hackers hate them! 😈
5.2. Thread Safety 🧵
No more race conditions! Strings are naturally thread-safe since they can’t be changed. Multi-threaded apps can breathe easy. 😌
6️⃣ But Wait… Strings Have Some Downsides Too 😱
6.1. No Customization (Final Class) 🚧
Want to extend String and add your own funky methods? Tough luck—it’s final! 😭
👉 Workaround: Use utility libraries like Apache Commons Lang or Guava. They’re like guitar effects pedals for strings! 🎛️
6.2. Sensitive Data Sticking Around 😬
Since strings are cached, passwords might linger in memory longer than you’d like. Solution? Use char[] instead!
char[] password = {'s', 'e', 'c', 'r', 'e', 't'};
This way, you can overwrite the array when done. 🔥
6.3. OutOfMemoryError? Yikes! 😵
The SCP is smaller than the heap, and if you overstuff it with literals, you might get an OutOfMemoryError.
👉 Avoid excessive string literals and consider using StringBuilder for concatenation-heavy operations! 🏗️
🎉 Final Encore: Keep Rocking with Java Strings
Java Strings are like legendary rockstars—immutable, efficient, and beloved by all! 🎸🔥 Keep them in mind when coding, and you’ll avoid memory issues while writing secure, thread-safe applications.
Until next time, Happy Coding & Keep Jamming! 🎶🚀